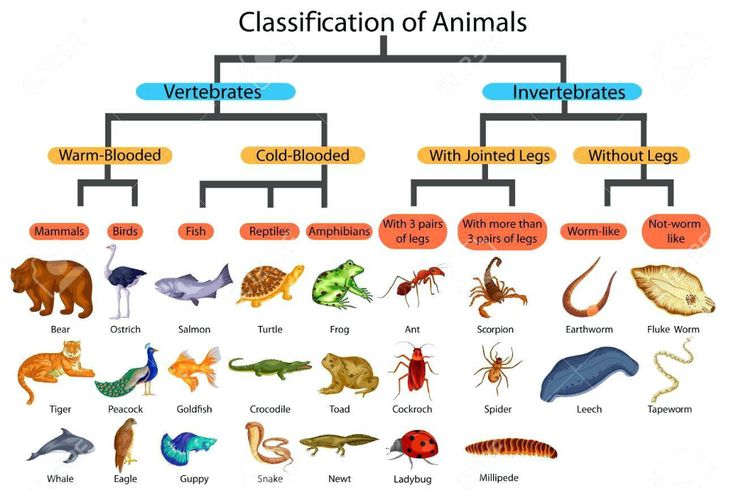
The phylum chordata (animals with backbone)is divided into five common classes thats are: 1: Fish. 2:Amphibians. 3:Reptiles. 4:Mammals. 5:Birds.
Fishes: 1: They live underwater. 2: They breath throughout gills. 3:Some of them have scales covering their bodies. 4:Fins help them to move under the water. 5:Cold-blooded animals. 6:They are born from egges. Amphibians: 1:Thin and humid skin. 2:Transformation throughout their life cycle. 3:They change their breathing method. 4: They are bron from egges. 5:Clod-blooded animal. 6:They live on the ground and water. Reptiles: 1:The longest lived species on the planet. 2:Cold-blooded animals. 3:The body covered with scales or shells. 4:They cannot chew . 5:They are born from eggs. 6:They live on the ground or in the water. Mammals: 1:They are born alive from the mother. 2:They breath through lungs. 3:They live in the water ,the air and the ground. 4: They have their body covered by fur. 5:They are warm-blooded. Brids: 1:Body covered with feathers. 2:They usually have porous lightweigh bones to allow them to fly. 3:They live flying or on the ground. 4:They have wings to fly. 5:Their mouths are toothless beaks. 6:Warm-blooded animals. 7:They are born from egges.
Vertebrates play a crucial role in the field of zoology for several reasons:
- Diversity: Vertebrates represent a highly diverse group of animals, ranging from fish and amphibians to reptiles, birds, and mammals. This diversity offers researchers a broad spectrum of organisms to study, providing insights into various biological and ecological aspects.
- Evolutionary Studies: Vertebrates have a well-documented evolutionary history that allows scientists to trace the development of anatomical structures, physiological functions, and behaviors. They provide a valuable framework for understanding the evolutionary relationships among different species.
- Biomedical Research: Many vertebrates, especially mammals, share physiological and genetic similarities with humans. This similarity makes them essential models for studying human diseases, genetics, and developmental processes. Insights gained from studying vertebrates often have direct implications for human health.
- Ecological Significance: Vertebrates play vital roles in ecosystems as predators, prey, and ecosystem engineers. They help maintain ecological balance and contribute to various ecosystem functions, such as nutrient cycling and seed dispersal.
- Conservation: Vertebrates often serve as flagship species for conservation efforts. Protecting habitats and populations of iconic vertebrates not only helps these specific species but also benefits entire ecosystems and other associated species.
- Economic Importance: Many vertebrates are economically important, whether through agriculture (livestock), fisheries, or as companion animals. Understanding their biology and behavior is crucial for managing these resources sustainably.
- Behavioral Studies: Vertebrates exhibit a wide range of behaviors, from complex social interactions to migration patterns. Studying their behavior provides insights into learning, communication, mating strategies, and social structures.
In essence, vertebrates are fundamental to the study of zoology because they offer a rich diversity of organisms that allow scientists to explore various aspects of biology, evolution, ecology, behavior, and their relevance to human life and the environment.