The human heart is a vital organ that plays a central role in the circulatory system. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. Here are some key facts about the human heart:
- Location: The heart is located in the chest, slightly to the left of the center. It is enclosed within the pericardium, a double-walled sac.
- Size and Shape: The human heart is roughly the size of a fist and has a conical shape. It weighs about 250 to 350 grams.
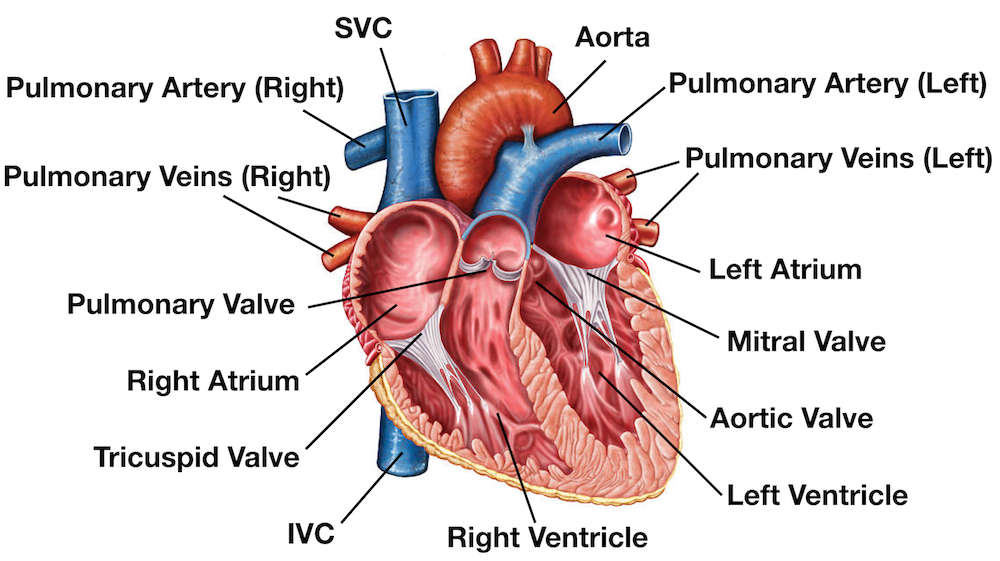
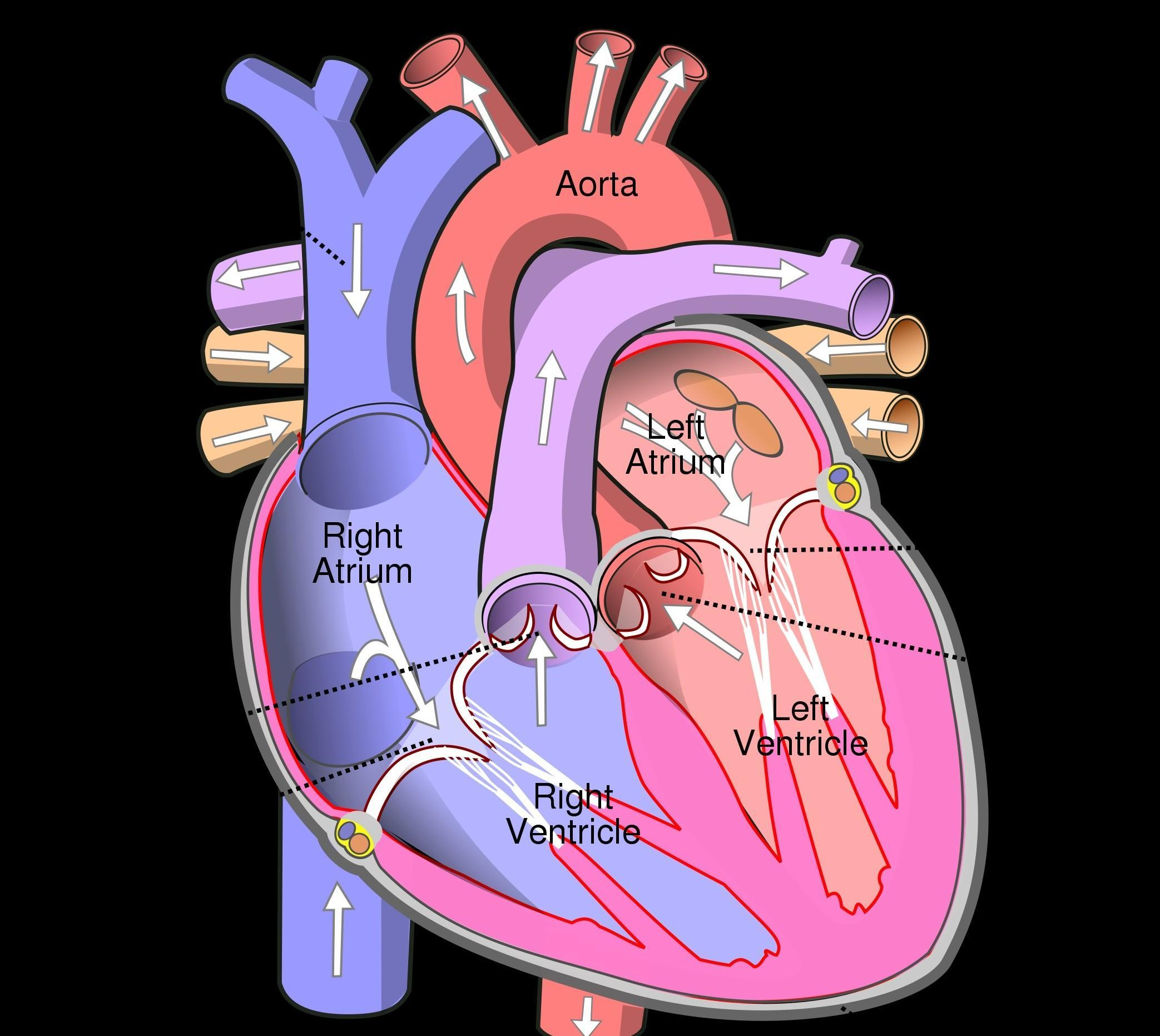
- Chambers: The heart is divided into four chambers – two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
- Valves: There are four valves in the heart – the tricuspid valve and the pulmonary valve on the right side, and the mitral valve and the aortic valve on the left side. These valves ensure the one-way flow of blood through the heart.
- Blood Vessels: The heart is connected to a network of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Blood Circulation: The heart is part of the circulatory system, which consists of the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation. In systemic circulation, oxygenated blood is pumped from the left ventricle to the body, and deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium. In pulmonary circulation, deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and returns to the left atrium.
- Heartbeat: The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles, known as the cardiac cycle, result in the heartbeat. The heart pumps approximately 60 to 100 times per minute at rest, but this rate can increase during physical activity.
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial for overall well-being, and lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can contribute to cardiovascular health. Various medical conditions, such as heart disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias, can affect the functioning of the heart and may require medical intervention.